mono2stereo-bench
1Dalian University of Technology 2ARC Lab, Tencent PCG 3The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
🔆 Brief introduction
💡 Abstract. With the rapid proliferation of 3D devices and the shortage of 3D content, stereo conversion is attracting increasing attention. Recent works introduce pretrained Diffusion Models (DMs) into this task. However, due to the scarcity of large-scale training data and comprehensive benchmarks, the optimal methodologies for employing DMs in stereo conversion and the accurate evaluation of stereo effects remain largely unexplored. In this work, we introduce the Mono2Stereo dataset, providing high-quality training data and benchmark to support in-depth exploration of stereo conversion. With this dataset, we conduct an empirical study that yields two primary findings. 1) The differences between the left and right views are subtle, yet existing metrics consider overall pixels, failing to concentrate on regions critical to stereo effects. 2) Mainstream methods adopt either one-stage left-to-right generation or warp-and-inpaint pipeline, facing challenges of degraded stereo effect and image distortion respectively. Based on these findings, we introduce a new evaluation metric, Stereo Intersection-over-Union, which prioritizes disparity and achieves a high correlation with human judgments on stereo effect. Moreover, we propose a strong baseline model, harmonizing the stereo effect and image quality simultaneously, and notably surpassing current mainstream methods.
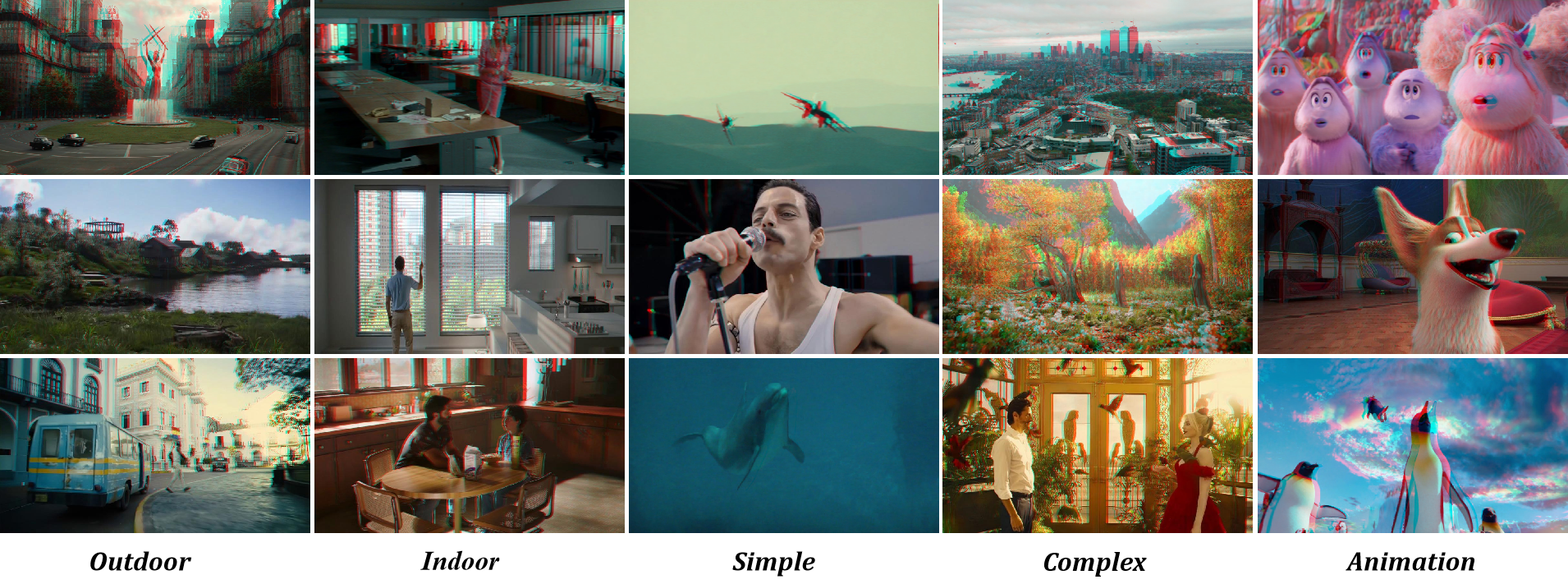

📦 Datasets. We collect approximately two million stereo image pairs for model training and provide the code for data processing.
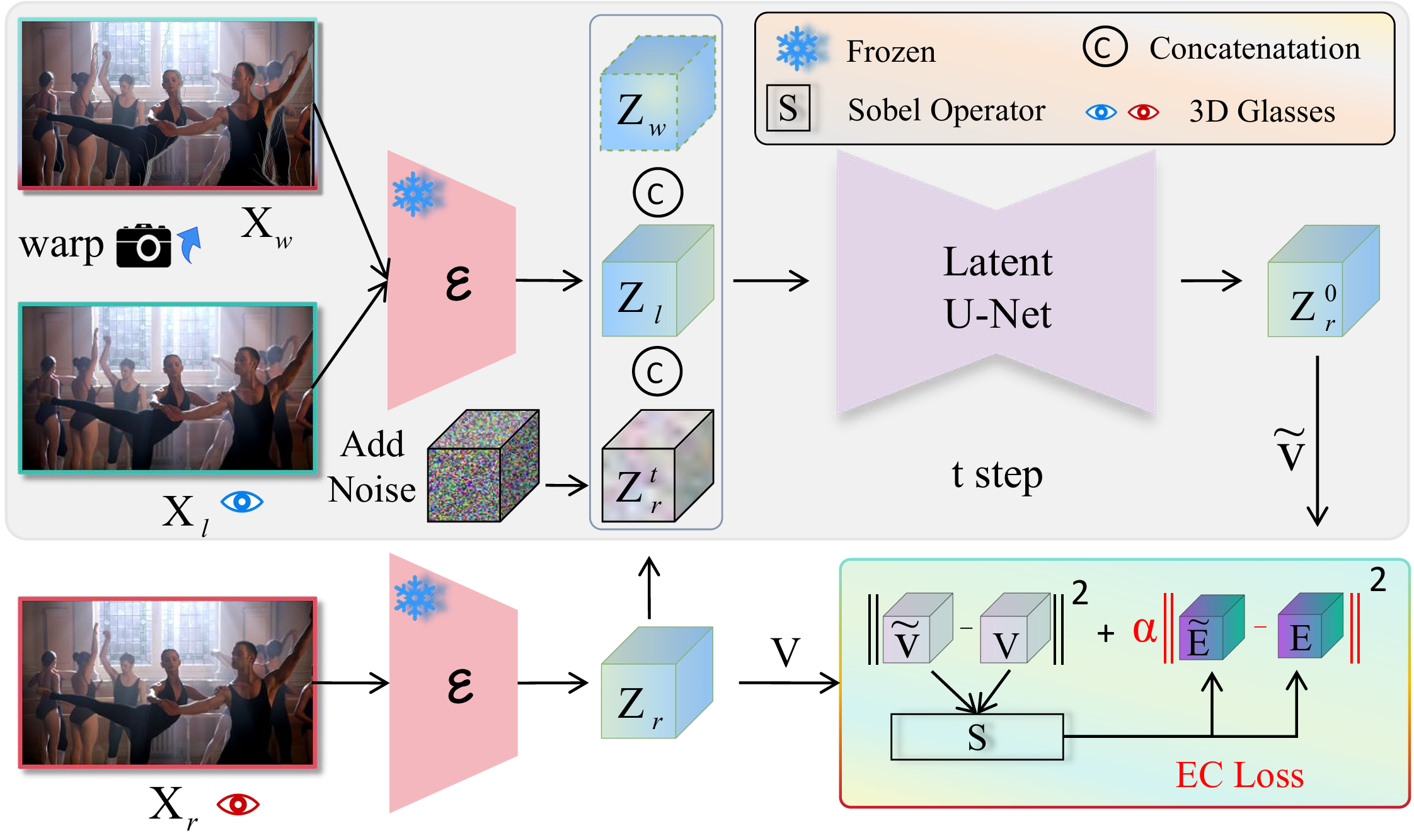
⛩️ Architecture. We find that due to the small differences between the left and right images, the model tends to degenerate into an identity mapping during training. Therefore, we add an edge consistency loss to force the model to focus on edge information.
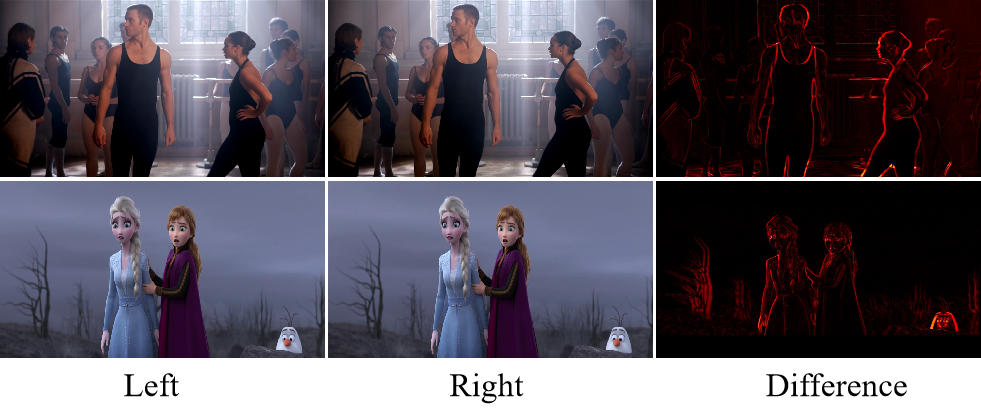

🧪 SIoU. We find that due to the small differences between the left and right images, the model tends to degenerate into an identity mapping during training. Therefore, we add an edge consistency loss to force the model to focus on edge information.
🎥 Visual Effects
👓 You can wear red-blue glasses to get the out-of-screen effect. 👓
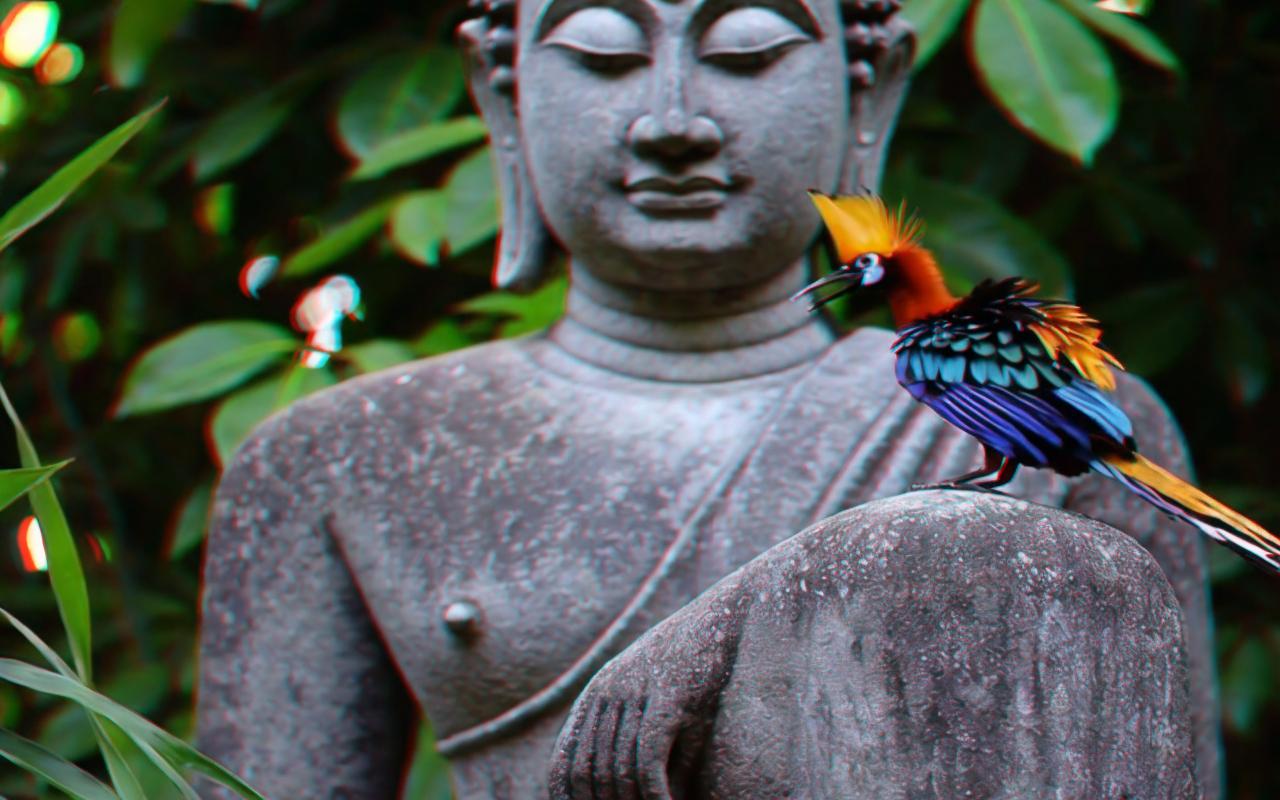
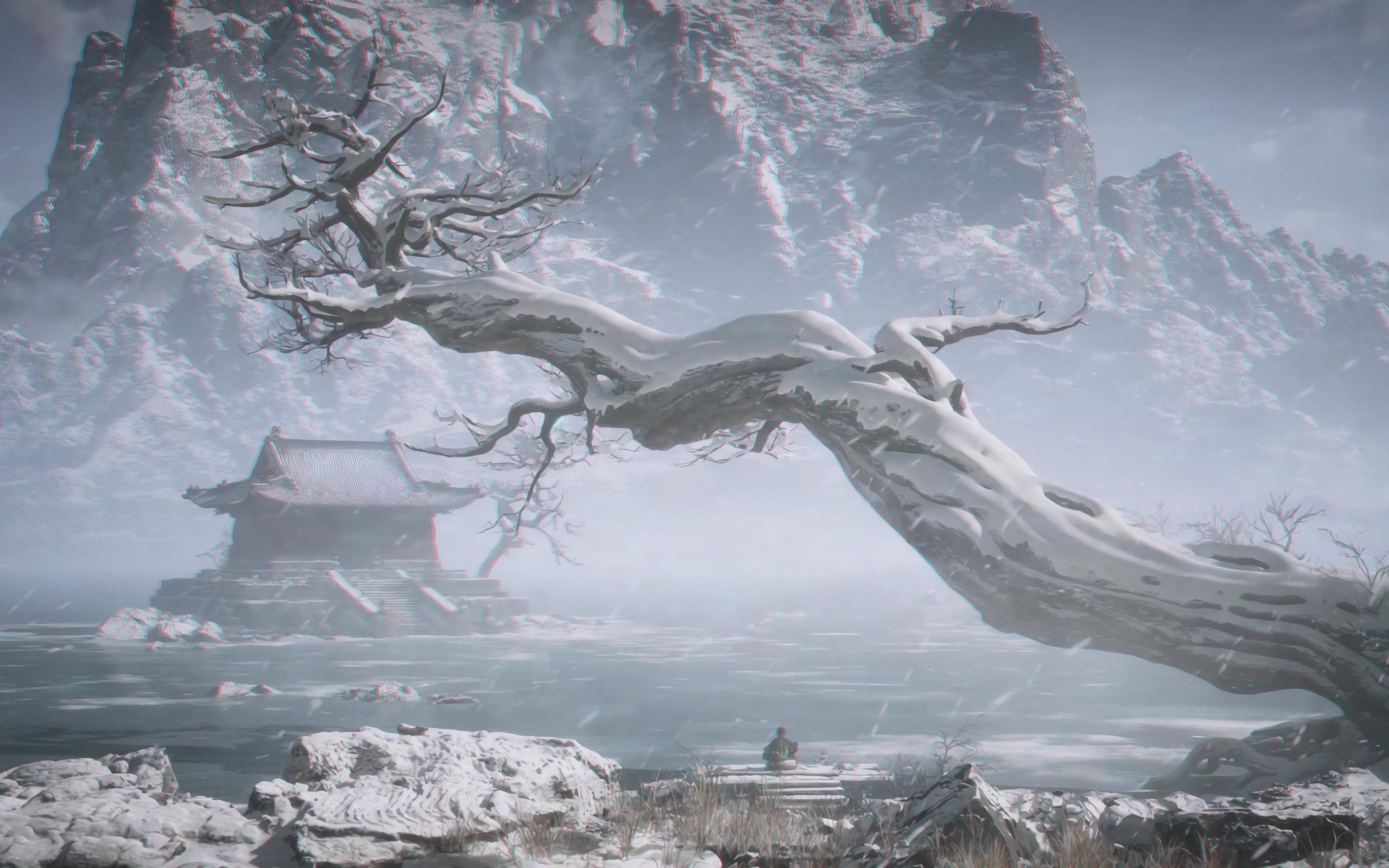
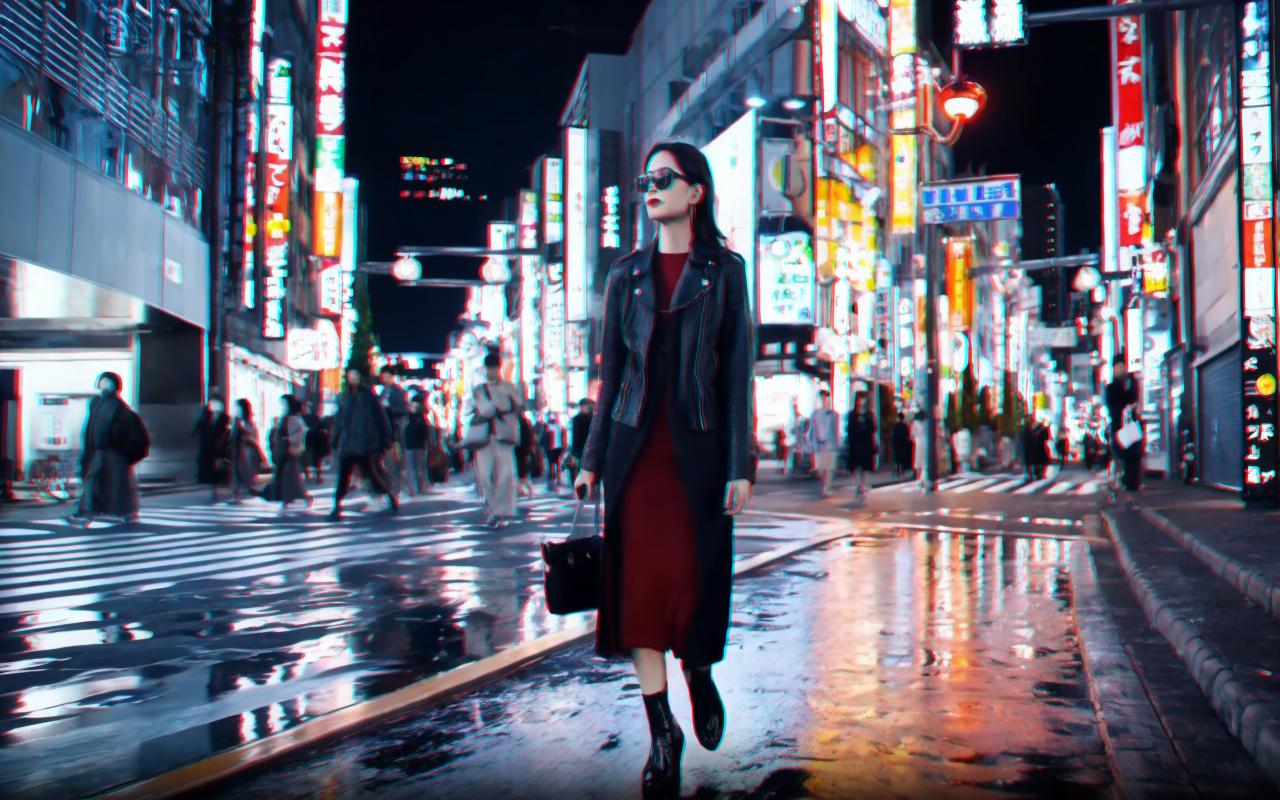
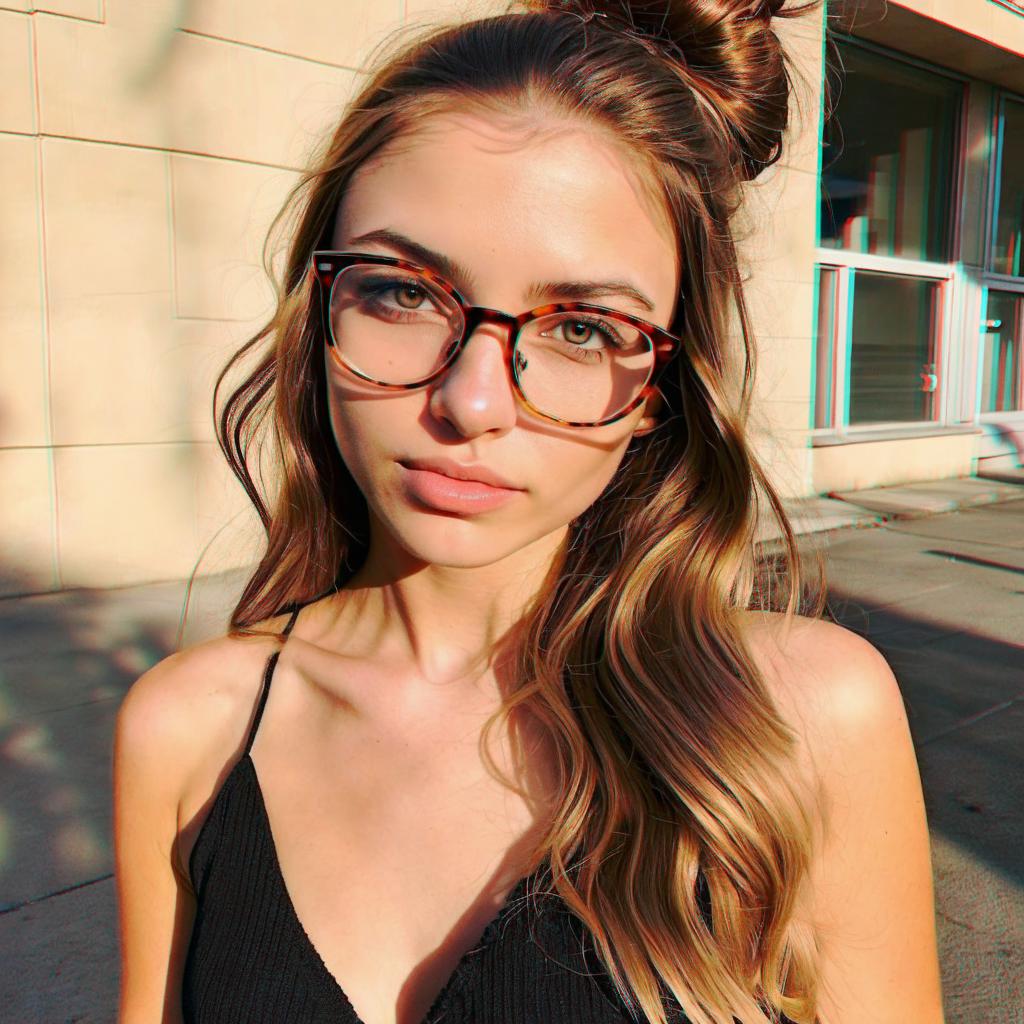





🔥 Exploring the Future
📢 It is important to note that our baseline model does not incorporate temporal information. Although it processes the input video frame by frame, the temporal consistency is not well-maintained, leading to flickering artifacts. In future work, we plan to train a video generation model specifically for stereo conversion tasks. The left panel shows the left-eye view, while the right panel displays the right-eye view generated by our baseline model.
Acknowledgements



